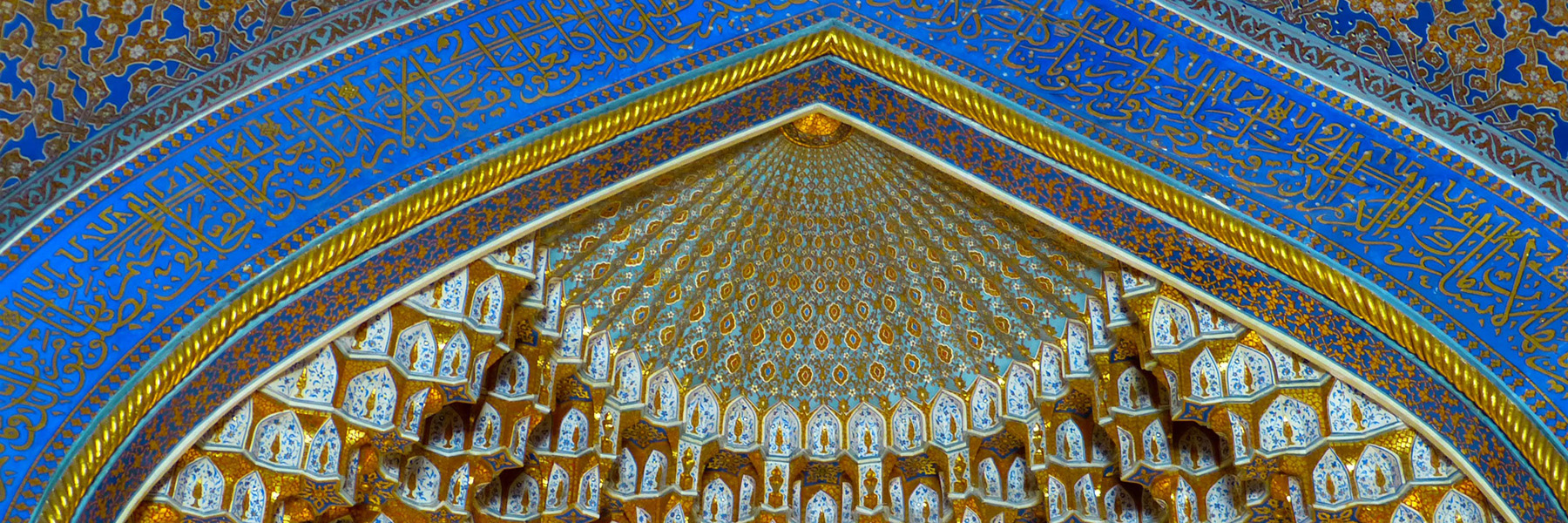
Located in the heart of Central Asia, Uzbekistan was a historic center of empires, education, and trade. Many cities in Uzbekistan were hubs on the ancient Silk Road, the famous trading route between China and the West.
Today, Uzbekistan is the second largest exporter of cotton after the U.S. and has rich natural resources: natural gas, oil, gold, copper, uranium, and others. Also, Uzbekistan is a strategically important country in Central Asia.
Uzbek is a Turkic language and the official language of Uzbekistan. It has about 35.3 million native speakers and belongs to the southeastern Turkic (or Karluk) family of Turkic languages, from which it gets its lexicon and grammar. Other influences stem from Persian, Arabic and Russian.
One aspect that distinguishes Uzbek from other Turkic languages is its rounding of the vowel /a/ to /ɒ/ or /ɔ/, a feature influenced by Persian.
Before the expansion of Russian and the Soviet Empires into Central Asia, Uzbek was written in an Arabic script. In 1940, Uzbek was switched to Cyrillic script due to Soviet policy. In the early nineties, the Uzbek government official reintroduced the Latin script, although the use of Cyrillic is still widespread.